Decoding the Social Dynamics of Prairie Dogs
Prairie dogs are often overlooked when discussing complex animal behavior, but these rodents have an intricate social system that rivals even those of higher mammals. This article delves into the fascinating world of prairie dogs, uncovering their sophisticated society and their surprising communication skills.

Prairie Dogs: A Brief History
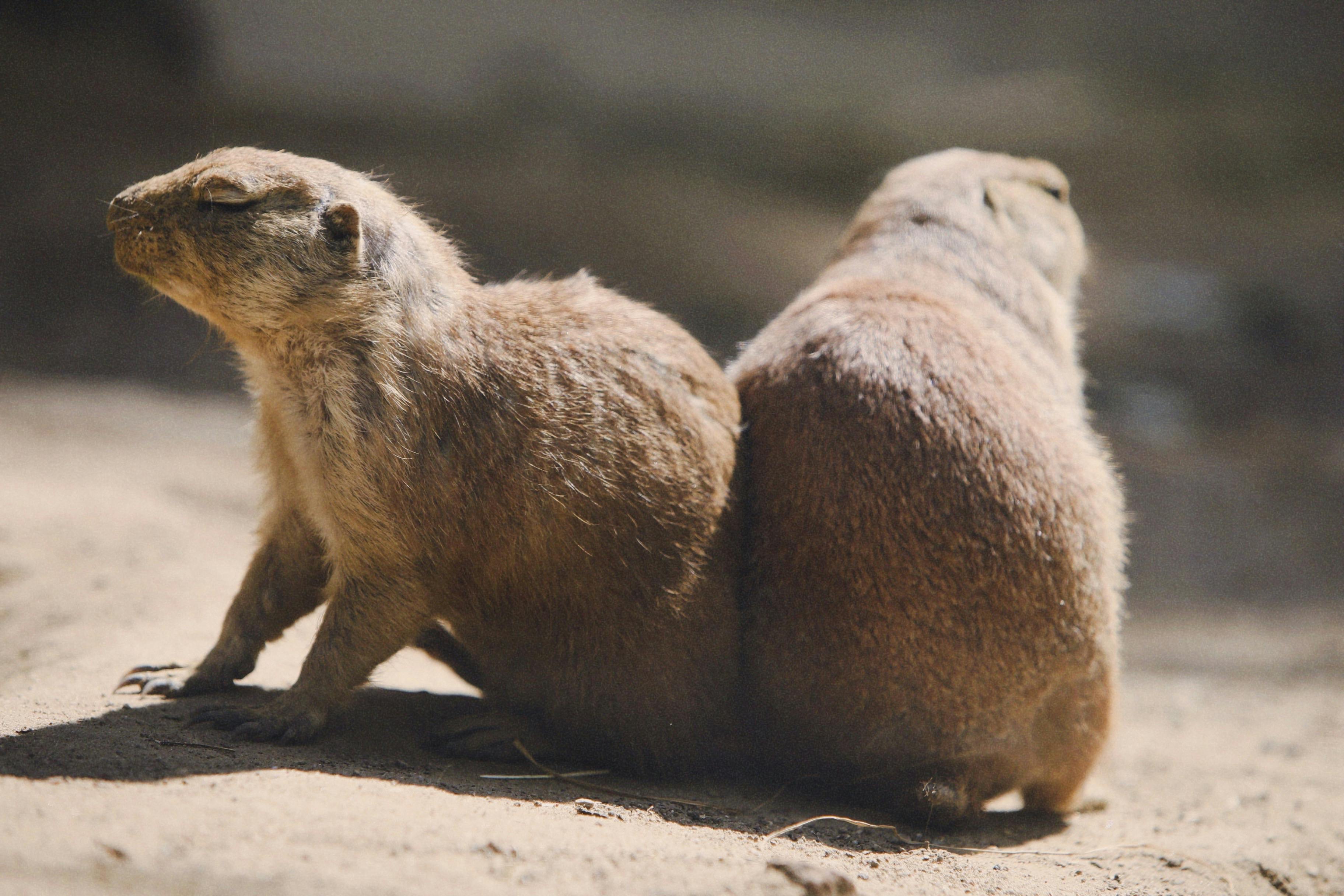
Prairie dogs are burrowing rodents native to North America’s grasslands. They are named for their habitat and the warning call they make, which sounds similar to a dog’s bark. There are five species of prairie dogs, and they are all members of the squirrel family. Historically, prairie dogs were seen as pests by farmers and ranchers because they can damage crops and create hazardous holes in pastures. However, their role in maintaining the ecosystem’s health is increasingly recognized.
The Complex Social Structure of Prairie Dogs
Unlike other rodents, prairie dogs live in extensive burrow systems, called towns, which can house hundreds of individuals. These towns are divided into smaller territories owned by family groups known as coteries. A coterie usually consists of one dominant male, several females, and their offspring.
Social interactions within the coterie are complex and involve a range of behaviors, including grooming and play. Aggression is typically reserved for prairie dogs from different coteries, highlighting the strong territorial instincts of these creatures.
Communication: More Than Just Barks
One of the most intriguing aspects of prairie dog behavior is their sophisticated communication system. Prairie dogs use a variety of calls to communicate with each other, and these calls can convey remarkably specific information. Research has shown that their calls can differentiate between different types of predators, their size, and even their speed. This level of detail in animal communication is rare, making prairie dogs a fascinating subject for behavioral scientists.
Current Status and Conservation Efforts
Despite their intriguing social dynamics, prairie dogs face several threats. Habitat loss due to agriculture and urban development has led to a significant decrease in their population. Additionally, they are often poisoned or shot due to their reputation as pests.
Conservation efforts are underway to protect prairie dogs and their habitats. These include relocating prairie dogs to protected areas, implementing non-lethal control methods, and educating the public about their ecological importance.
In Conclusion
Prairie dogs offer a captivating glimpse into the complexity of animal behavior. Their intricate social structure and sophisticated communication system serve as a testament to the richness of life even among the smallest creatures. By protecting these remarkable rodents, we are preserving not only a unique species but also the fascinating world of animal behavior that they represent.